A finite element - discrete element model
for viscoelastic suspension
M.Henry, J.Lambrechts, V.Legat



www.migflow.be
An Unresolved DEM-FEM model
- Solid phase
Discrete element
Lagrangian representation
Insight in contacts physics
- Fluid phase
Continuous medium
Eulerian representation
Computational convenience
- Fluid-grains interaction
Empirical momentum transfer
Parametrization are required
- Averaged Navier-Stokes equations, $\mathbf{u} = (1-\phi) \mathbf{v}$, $\mathbf{u}^s = \phi \mathbf{v}^s$ \[\begin{aligned} \nabla \cdot \mathbf{u} + \nabla \cdot \mathbf{u}^s &= 0\\ \rho\left(\frac{\partial \mathbf{u}}{\partial t} + \nabla \cdot \frac{\mathbf{u u}}{1-\phi}\right) &= \nabla \cdot \left(-p\mathbf{I} + 2\eta^*\mathbf{D}\right) + \mathbf{f} + (1-\phi) \rho \mathbf{g}\\ \end{aligned} \]
- Drag parametrization \[ \mathbf{f} = g(\phi) C_d \pi r^2 \frac{\rho}{2} \left\lVert \mathbf{v^s} - \mathbf{v} \right\rVert \left( \mathbf{v}^s - \mathbf{v} \right) \]
- Subgrid scale viscous model \[ \eta^* = \eta\ \underbrace{(1+2.5\phi + 5\phi^2)}_{\text{Batchelor model}} \]
An implicit method for the contacts
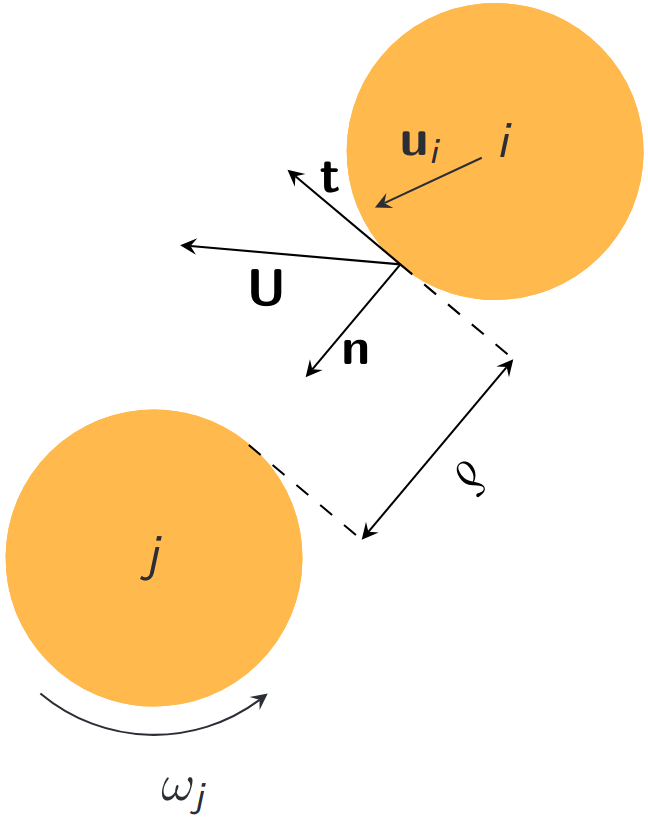
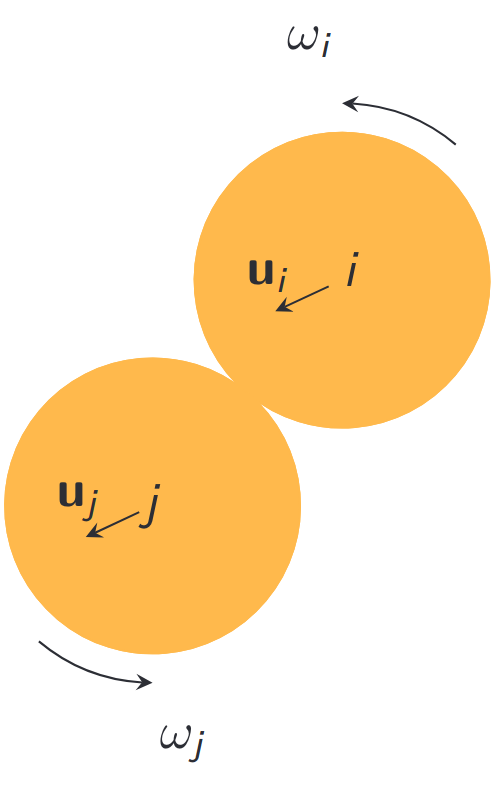
- Newton's second law \[ \frac{d (m_k \mathbf{u}_k)}{d t} = m_k\mathbf{g} - \mathbf{f}_k \]
- Dynamics equation \[ \mathbf{M}\Delta \mathbf{u} = \mathbf{p} \]
- Local Frame \[ \mathbf{U} = \mathbf{H}\mathbf{u} \hspace{5mm} \mathbf{P} = \mathbf{H} \mathbf{p} \]
- Solve for $\mathbf{P}$ \[ \begin{pmatrix} \Delta U_n \\ \Delta U_t \end{pmatrix} = \underbrace{\begin{pmatrix} w_{nn} & 0 \\ 0 & w_{tt} \end{pmatrix}}_{ \mathbf{H}\mathbf{M}^{-1}\mathbf{H}^T} \begin{pmatrix} P_n \\ P_t \end{pmatrix} \]
- Normal and tangential components \[ \begin{aligned} P_n &= \frac{1}{w_{nn}}\text{max}(0, U_n - \frac{\delta}{\Delta t})\\ P_t &= \frac{1}{w_{tt}}\text{min}(|U_t|, \frac{w_{tt}}{w_{nn}}\mu |U_n|)\frac{U_t}{|U_t|} \end{aligned} \]
- Update velocities \[ \mathit{u} \rightarrow \mathit{u} + \mathbf{M}^{-1}\mathbf{H}^T \mathbf{P} \]
Objectives
Is unresolved approach suitable
to study visco-elastic properties ?
to study visco-elastic properties ?
How to model cohesive interactions
and clustering for colloidal suspension ?
and clustering for colloidal suspension ?
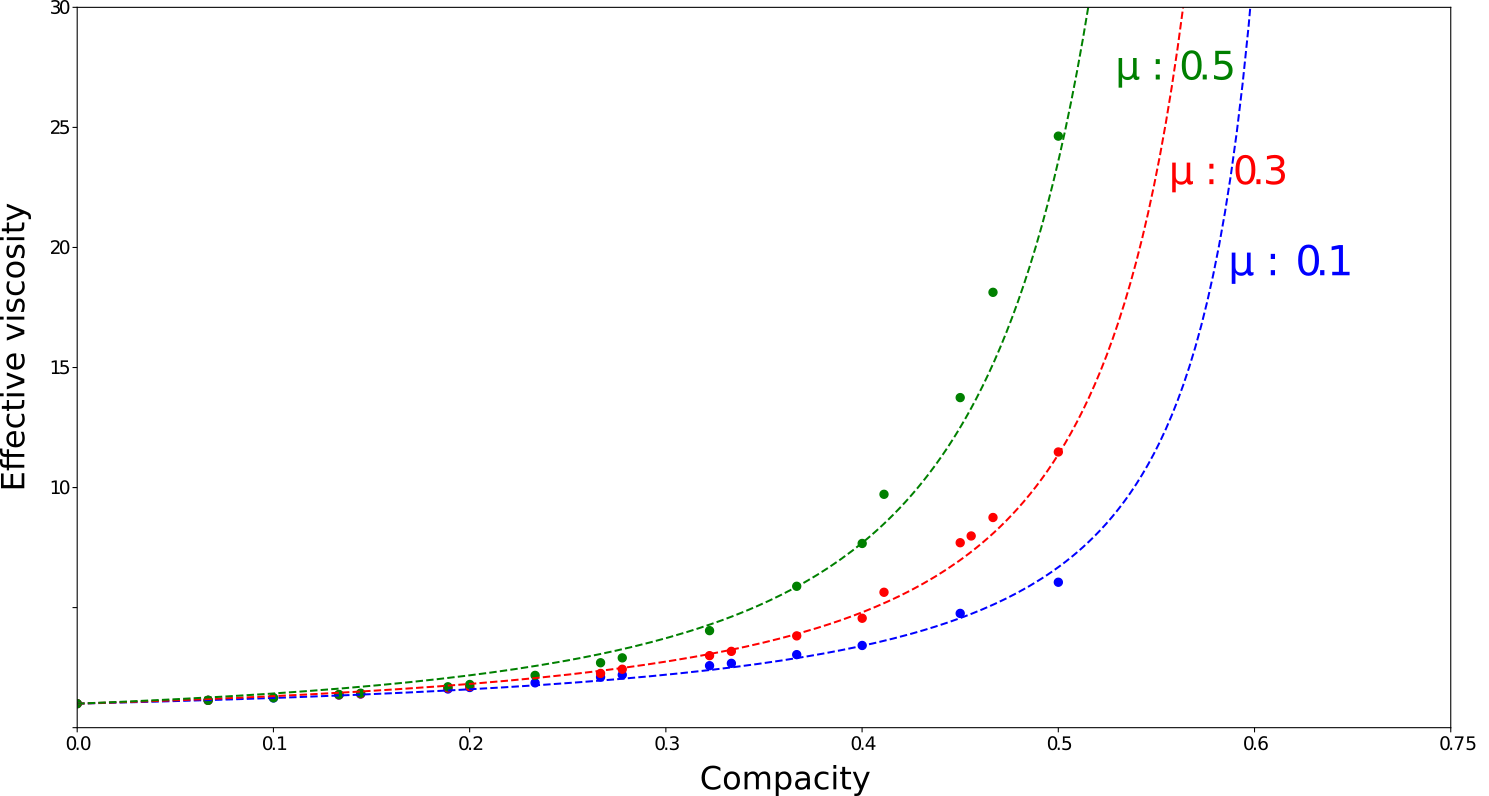
Effective viscosity under a simple shear flow
Effective viscosity follows Krieger curves
\[
\eta_r = \left(1 - \frac{\phi}{\phi_c}\right)^\alpha
\]
Contact dynamics allows to study cohesive materials
-
Forces can be added into a particle-particle contact to study agglomeration phenomenon.
Force derivated from Morse's potential : \[U_{morse}(r) = D_e \left[1 - e^{-\beta d \left(\frac{r}{d}-1\right)}\right]^2\]

Constitutive law proposed by A.Yazdani[2017]
An over-simplified model
for platelet interaction
Thrombus formation by Simon Yans
Which particle-particle law should we used ?
How to deal with parameters uncertainty ?
How to activate cohesive law based on a unresolved model ?
How to deal with parameters uncertainty ?
How to activate cohesive law based on a unresolved model ?
Predefined bond for particle chains
-
Each chain is pre-generated contacts with a cohesive spring force based on a FENE model :
\[
\begin{aligned}
F_{s} = \frac{k \Delta \mathbf{x}}{1 - \left(\frac{\Delta\mathbf{x}}{Q}\right)^2}
\end{aligned}
\]
Conclusion
- Unresolved multi-scale model is suitable to study visco-elastic properties of suspension
- Cohesive particles and elongated chain can be modelled by the contact dynamics
- Is this toy model suitable to study hard sphere colloids ?